Are We Ingesting Plastics Every Day? The Truth About Microplastics KellyOnTech ESG Series
Would you believe it if someone said that we are ingesting plastics every day?
The answer is yes, but the plastics are small pieces, less than 5 mm in length, known as microplastics.
Let’s take a quiz, which of the following five options contain microplastics?
- Honey
- Sea salt
- Beer
- Tap water
- Dust in the house
The answer is that all of them contain microplastics.
What Are Microplastics?
Microplastics are formed in a variety of ways, the most common being various types of plastic waste. Larger pieces of plastic degrade into smaller and smaller pieces, which are ingested by oceans, lakes, soils, air and various organisms.
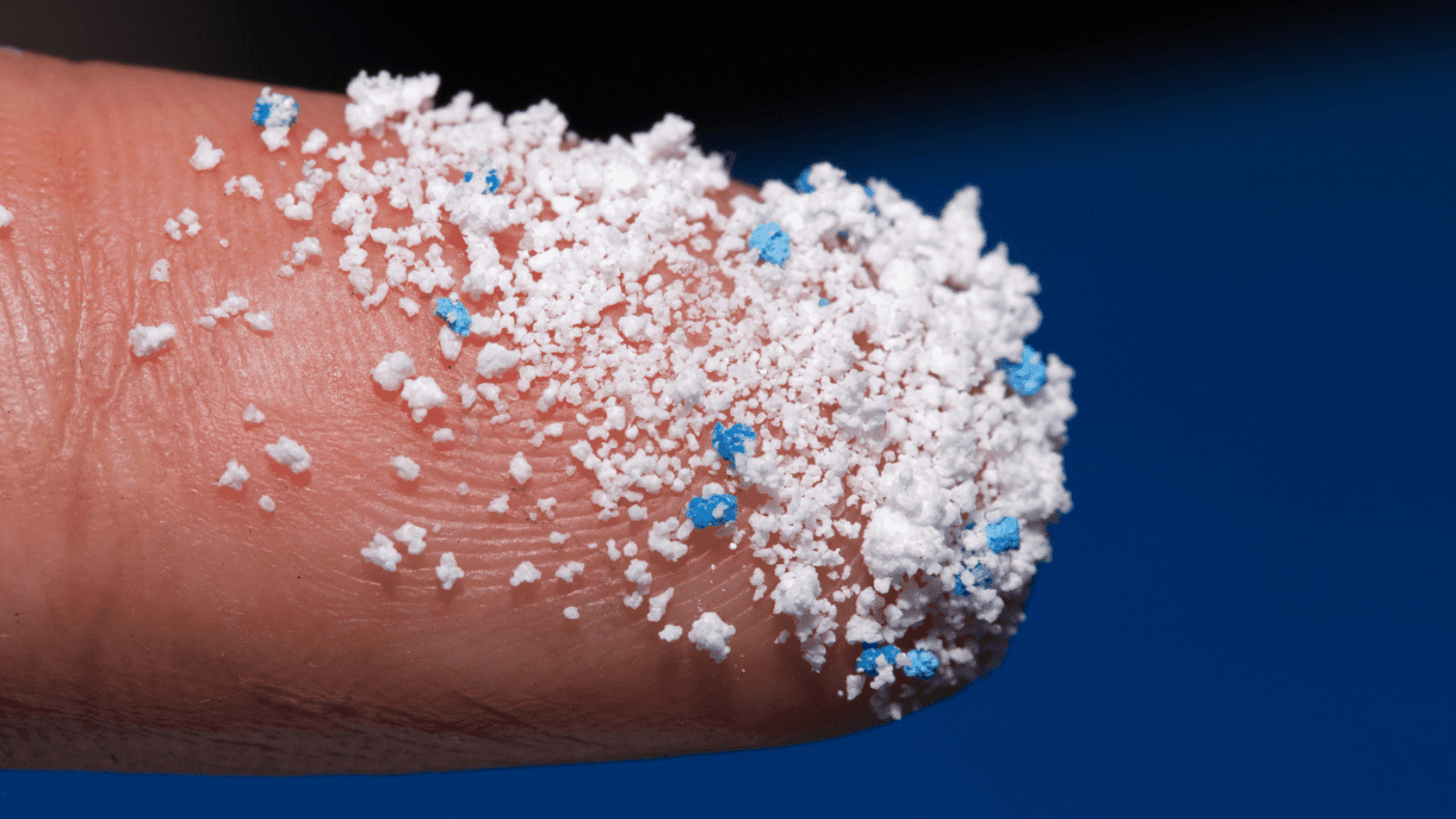
Another type of microplastics is directly produced. An example is microbeads. It is very tiny pieces of man-made polyethylene plastic that is added as an exfoliator to health and beauty products, like the toothpaste we use every day. These tiny particles can easily pass through water filtration systems and end up in the oceans and large lakes, where they are ingested as food by aquatic life, posing a potential life threat. China’s deep-sea probe “Jiaolong” once discovered microplastics at a depth of 4,500 meters under the sea.
Microbeads are not a recent problem. According to the United Unions Environment Program,microbeads first appeared in personal care products about fifty years ago, and they are increasingly replacing natural ingredients. In 2015, microbeads were banned in the United States, but microplastics are still allowed.
Are Microplastics Harmful to Humans?
Since microplastics have been around for so long, is it harmful to the human body?
Although the impact of microplastics on human health is not fully understood, there are at least two reasons why we should be cautious about their presence in the environment.
First, microplastics can enter various ecosystems, including oceans, rivers and soils, where they are ingested by marine animals, birds and other wildlife. Studies have shown that ingesting microplastics can lead to physical harm, such as blockages in the digestive system or organ damage.They can have indirect effects, such as altering an animal’s eating behaviour or causing hormonal changes.
Second, there is evidence that microplastics can act as carriers for other pollutants. Due to its small size and large surface area, it can absorb and accumulate toxic substances such as heavy metals and organic pollutants. When these contaminated microplastics are ingested by organisms, there is a risk of transferring these pollutants up the food chain.
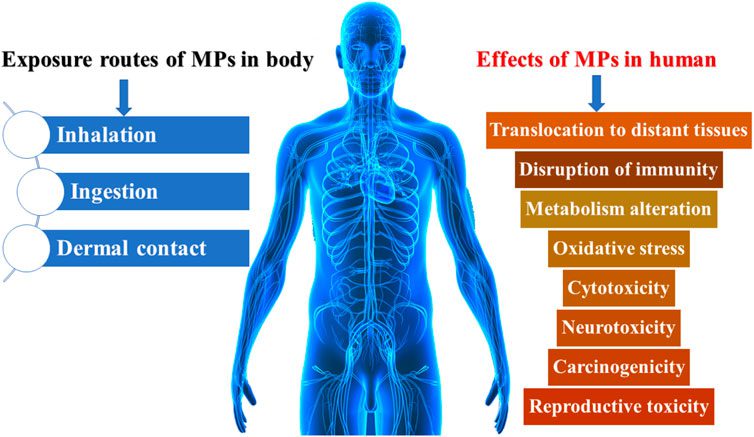
Overall, although the full extent of the harm caused by microplastics is unknown, there is growing evidence that they may have negative impacts on ecosystems and may pose risks to human health. Efforts to reduce plastic pollution and promote plastic waste management are critical to addressing this issue.
Which Companies Make Products that Reduce Microplastics?
Samsung Electronics unveiled a washing machine at this year’s Consumer Electronics Show, CES 2023, that uses less microfiber circulation and filtration technology. The technology reduces microplastics emissions by 54% and prevents microplastic particles from escaping into the ocean at the end of the wash cycle. This washing machine is being sold in South Korea and the United States from February 2023 and will gradually be rolled out in Europe.

In recent years, Haier has begun to focus on the development of efficient use of laundry detergent, improving the service life of clothes, and reducing the emission of microplastics from clothes, while promoting energy saving and consumption of washing machines.

On April 27, the 2023 China Home Appliances and Consumer Electronics Expo (AWE 2023) opened in Shanghai. Haier Washing Machine and China Standardization Association took the lead, jointly with the China Household Institute (Beijing) Certification Co., the Chinese Research Institute of Daily-use Chemical Industry and and the China Household Electric Appliances Research Institute released the industry’s first “Green Cleaning and Care Technical Requirements for Washing Machines”, which stipulates the definition of greenwashing, technical requirement, star rating evaluation requirements and test methods.
What Technologies Are Available to Reduce Microplastics?
In 2020, researchers at the University of Lethbridge in Australia developed a new nanotechnology process that can convert plastic waste into two valuable products: graphene ( a molecular compound used to strengthen electronics and composites) and hydro ( a type of clean fuel). While the discovery is still under development, the conversion from plastic to graphene is more cost-effective, because the material does not need to be cleaned or sorted before processing. By simplifying the collection and disposal of recyclables, more products can be recycled.

Australian researchers also created nanocoils, which are reusable nanoscale reactors made of carbon nanotubes and metals that are about half the width of a human hair. When in contact with microplastics, these nanocoils trigger a chemical reaction that breaks the microplastics down into their molecular components. The resulting material no longer contains plastics, but only consists of carbon dioxide and water. Nanoscale carbon-based molecular components can be used as a food source for plant life such as algae, and preliminary tests have shown improved plant growth in the observed environment. This innovative approach converts microplastics into valuable nutrients by breaking down into their core components before they enter the environment.
Researchers in the Czech Republic are also deploying nanotechnology to fight microplastics, but they are taking it a step further by using solar-powered microrobots. These microrobots utilize a photocatalytic degradation process, using reactants such as polylactic acid and polycaprolactone to break down microplastics into basic components — carbon dioxide and water — to ensure they don’t harm marine life. These autonomous microrobots offer a key solution to the problem of microplastics in hard-to-reach areas, and their solar-powered operation requires minimal maintenance.
Tag:ESG trends, KellyOnTech, technology